The Mediterranean Diet Plan, Explained by Rachael Ray
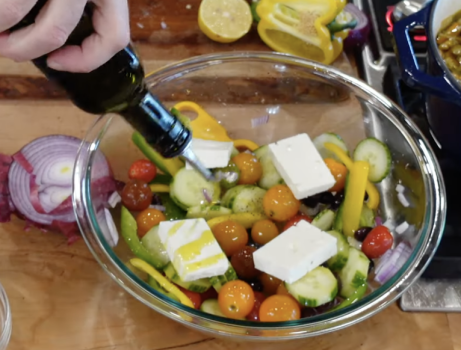
In recent years, the Mediterranean diet has gained popularity as a healthy and balanced way of eating.
Originating from the traditional eating habits of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, this diet has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including weight management and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. So what exactly is the Mediterranean diet plan, and why has it become so popular? In this article, we’ll take a closer look at this dietary pattern and break down its components.
What is the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet has been around for centuries, but it wasn’t until the 1960s that it gained attention in the scientific world. Researchers noticed that people from the Mediterranean region had lower rates of heart disease and other chronic illnesses, and they attributed this to their diet. The Mediterranean diet is based on the eating habits of countries like Greece, Italy, Spain, and Morocco. It emphasizes the consumption of plant-based foods, healthy fats, and moderate amounts of protein.
What Can You Eat on the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet is a primarily plant-based diet, with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds forming the basis of daily meals. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, making them essential for good health. On this diet, it is recommended to consume a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, such as tomatoes, leafy greens, berries, and cruciferous vegetables.
Healthy fats are a crucial component of the Mediterranean diet. Olive oil is the primary source of fat, and it is used in cooking and as a salad dressing. Other sources of healthy fats include avocados, olives, and nuts, which provide monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, known to promote heart health.
Whole grains, such as whole-grain bread, pasta, and rice, are also a staple in the Mediterranean diet. These foods are rich in fiber and provide essential nutrients such as B vitamins and minerals. Legumes, including beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are also an important part of this diet. They are excellent sources of plant-based protein and help to increase satiety.
The Mediterranean diet also includes moderate consumption of seafood, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Red meat is consumed in small amounts, no more than a few times a month. Fish, especially fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel, are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health.
What To Avoid on the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet avoids highly processed and refined foods, such as white bread, sugary drinks, and processed meats. These foods tend to be high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, and sodium, which can contribute to weight gain and chronic disease.
Additionally, the Mediterranean diet limits the consumption of saturated and trans fats typically found in butter, fatty meats, and fried foods. These unhealthy fats can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
How to Follow the Mediterranean Diet?
One of the best things about the Mediterranean diet is that it can easily be adapted to suit individual preferences and dietary needs. The emphasis is on whole foods and a variety of plant-based foods, so meals can be tailored to include personal favorites. The Mediterranean diet also encourages cooking meals at home using fresh and simple ingredients, making it a more sustainable and enjoyable way of eating.
It is essential to note that along with a healthy diet, regular physical activity is a crucial component of the Mediterranean lifestyle. Taking a walk after meals, practicing yoga or other forms of exercise can help to maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
In conclusion, the Mediterranean diet is a well-balanced, plant-based dietary pattern that has been shown to have numerous health benefits. By incorporating a variety of plant-based foods, healthy fats, and limiting processed and unhealthy foods, this eating plan promotes a healthy weight and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. So why not try incorporating some Mediterranean-inspired meals into your diet and reap the benefits of this traditional and wholesome way of eating.










Hooded Eyes Do’s & Don’ts!
DELICIOUS 20-minute meals » vegan + healthy
After watching this, your brain will not be the same
63 Year Old Man Reveals Secrets for a Flat Stomach
Healthy Vegan School Lunch Ideas – BENTO BOX